|
 Home
Page Home
Page
 The
Concept of Allah (God) The
Concept of Allah (God)
 What
is Islam? What
is Islam?
 Main
Pillars of Islam Main
Pillars of Islam
 Muslim
World Population Muslim
World Population
 The
Universal Religion The
Universal Religion
 Muhammad
(Peace Be Upon Him) Muhammad
(Peace Be Upon Him)
 Relevance Relevance
 Women
in Islam Women
in Islam
 The
Concept of Peace and War The
Concept of Peace and War
 Tolerance
in Islam Tolerance
in Islam
 Islam
and Cleanliness Islam
and Cleanliness
 Other
Religions Other
Religions
 Islam's
contribution to Humanity Islam's
contribution to Humanity
 Islam
and Knowledge Islam
and Knowledge
 Human
Rights in Islam Human
Rights in Islam
 History History
 sources sources
 Favourite
Links Favourite
Links
 Photo
Album Photo
Album
 About
Us About
Us

|
-
- Islam
is not a new religion, but the same truth that God
revealed through all His prophets to every people. For a
fifth of the world's population, Islam is both a
religion and a complete way of life. Muslims follow a
religion of peace, mercy, and forgiveness, and the
majority have nothing to do with the extremely grave
events which have come to be associated with their faith.
-
- The first revelation
to prophet Muhammad marked the beginning of
Islamic history. It was in the year 610. At that
time, a few people converted to Islam secretly in
Makkah lest they be tortured or killed. Later, in
622 AD, God revealed to Muhammad
that he and his followers should emigrate to
Madinah, 260 miles Northeast of
Makkah. There, Islam found great support
and an Islamic state was established.
-
-
- The year 622
is known as the Hijrah, or migration, the date
from which the Islamic calendar started.
-
- The year of migration
thus marks the first year of the new Islamic calendar. In
the next two years, the new religion found its way into
the hearts of more and more people. Religious practices
became established and a revealed law governed all
relationships within the Madinan community, which
now was securely established.
- By 632, the
whole of Arabia had accepted Islam as its
religion. In the same year, Muhammad died and
Abu Bakr, the most trusted friend, was elected to
be the first Caliph after the prophet's death. At
the time of the second Caliph, Omar Ibn
Al-Khattab, Islam spread very
rapidly.
-
- By 650,
Islam had reached both the Persian and the
Roman empires. Jerusalem, Persia, and
Egypt became Islamic countries. In the sixth
century, Islam reached Spain and
France. At the same time, Islam had been
spreading in Asia until it reached the islands
known today as the Philippines and
Indonesia via merchants and businessmen who were
able to spread Islam by their good conduct and behaviour.
In brief, Islam spread into Asia and Africa
as well as Europe in less than 150 years,
either by war with armies when they tried to prevent
Muslims from calling people to Islam or by
providing good examples of high morals and fair treatment
to all other peoples. In both cases, there was not a
single case of compelling a non-Muslim to convert to
Islam.
-
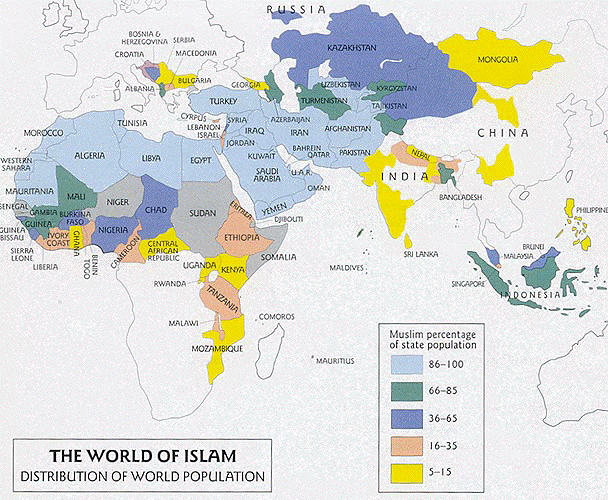
- Muslims now form a
very large nation that includes more than 1
billion people spread throughout the world. One billion
people from a vast range of races, nationalities and
cultures across the globe
- About 18% live
in the Arab world; the world's largest Muslim
community is in Indonesia; substantial parts of
Asia and most of Africa are Muslim
.
-
- Within a few years,
great civilisations and universities were flourishing,
for according to the Prophet,
'seeking knowledge
is an obligation for every Muslim man and
woman'. The
synthesis of Eastern and Western ideas and of new thought
with old, brought about great advances in medicine,
mathematics, physics, astronomy, geography, architecture,
art, literature, and history.
-
- Many crucial systems
such as algebra, the Arabic numerals, and
also the concept of the zero (vital to the
advancement of mathematics), were transmitted to medieval
Europe from Islam. Sophisticated instruments which were
to make possible the European voyages of discovery were
developed, including the astrolabe, the
quadrant and good navigational maps.
-
Spread Of Islam
- The Qur'an
records that Muhammad was the Seal of the Prophets, the
last of a line of God's messengers that began with
Adam and included Abraham, Noah, Moses,
and Jesus. He left for the future guidance of
the community the words of God revealed to him and
recorded in the Qur'an, and the sunnah, the
collective name for his opinions and decisions as
recorded in the tradition literature
(Hadith).
 -
|

![]()